Autoantibodies against the neuronal targets measured by the Cunningham Panel™ were selected based upon their biological association with specific neurologic and psychiatric symptoms.
Listed below are various symptoms which tend to correlate with specific test results in our clinical laboratory patient population analysis.
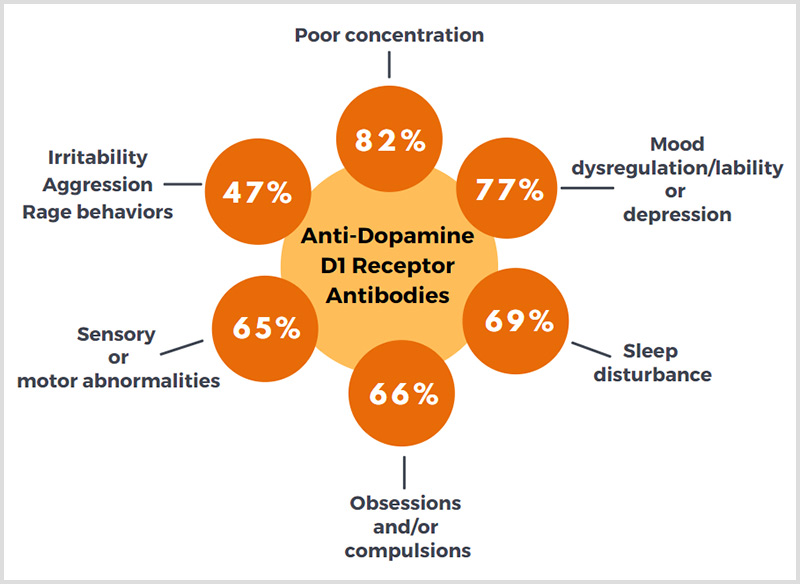
Anti-Dopamine D1 Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine 1 (D1) receptor were found to experience the following:
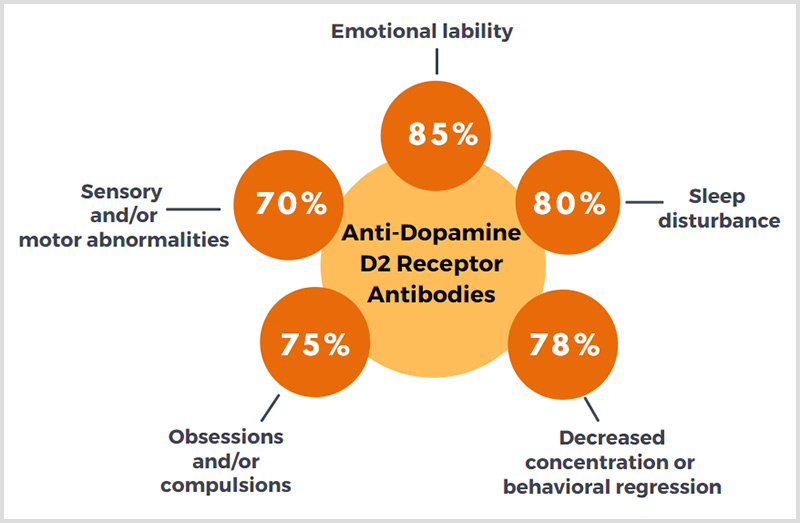
Anti-Dopamine D2L Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine 2L (D2L) receptor were found to experience the following:
These patients are likely to experience motor or movement disorders, including choreiform movements, new onset or exacerbations of hyperactivity, and impulsive behaviors, such as self-injurious or risky behaviors.
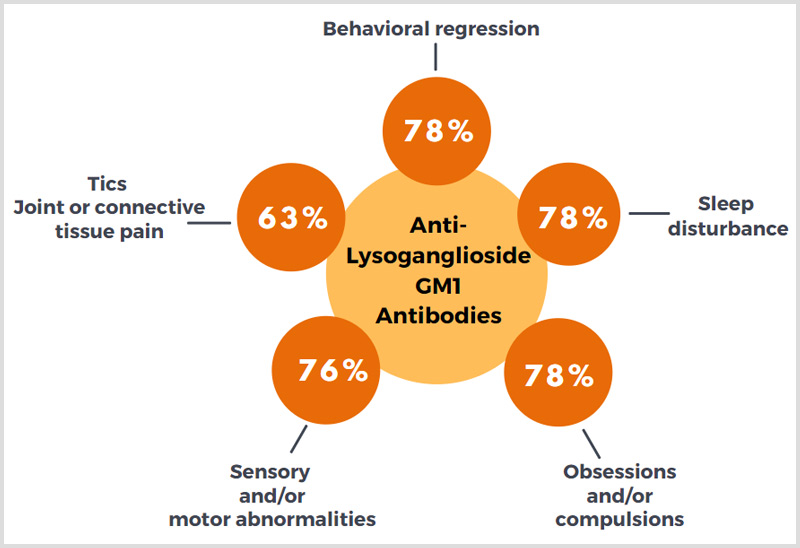
Anti-Lysoganglioside GM1 Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Lysoganglioside GM1 were found to experience the following:
These patients frequently experience tics (63%) and joint or connective tissue pain, as reported by physicians who regularly order the Cunningham Panel™.
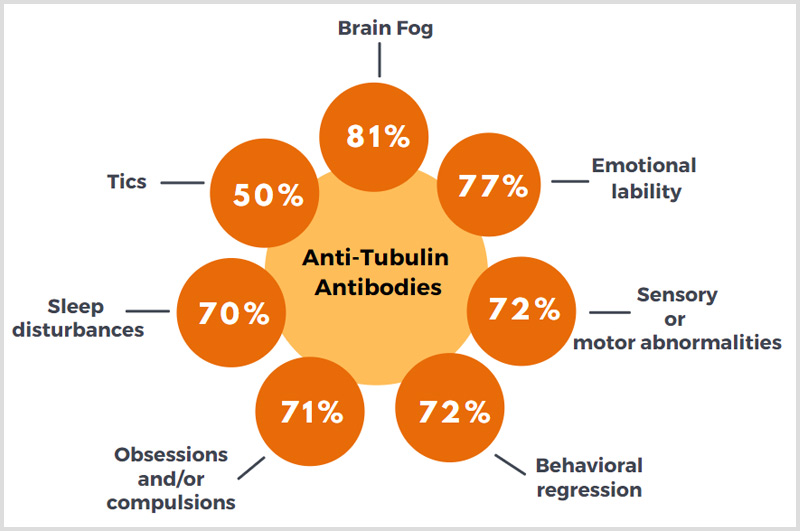
Anti-Tubulin Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Tubulin were found to experience the following:
Children are unlikely to use the term “brain fog.” These behaviors may be observed as inattentive, disengaged, “tuned out,” or they may struggle with concentration, memory and comprehension.
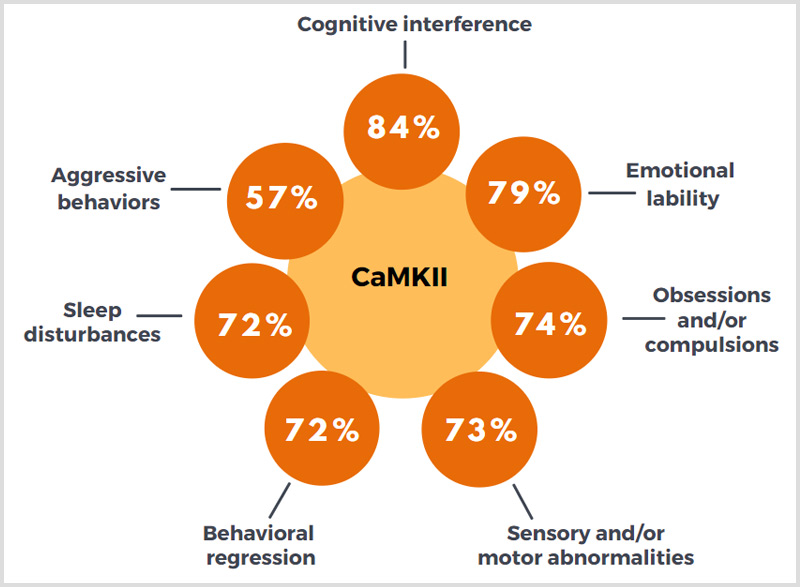
CaMKII – A Cell Stimulation Assay
Elevated levels in CaMKII results tend to correlate with involuntary movements which can be brief and of low amplitude.
Elevated levels also correlated with either early-stage illness, or potential re-activation of a previous infection, or onset of a new infection.
An elevated CaMKII result indicates a patient’s autoantibodies are stimulating this enzyme. CaMKII is responsible for upregulating brain neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
CaMKII activation may result in disrupted neuronal functioning, and trigger a variety of neurologic and/or psychiatric symptoms. Patients may experience mydriasis (dilation of the pupils), fight or flight behavior, increased pulse rate, and anxiety.
Borderline or low CaMKII may indicate a subclinical or occult chronic infection.
Patients with elevated CaMKII levels reported the following:
Learn More About The Cunningham Panel™
Overview Of The Cunningham Panel™
What does the Cunningham Panel™ measure?